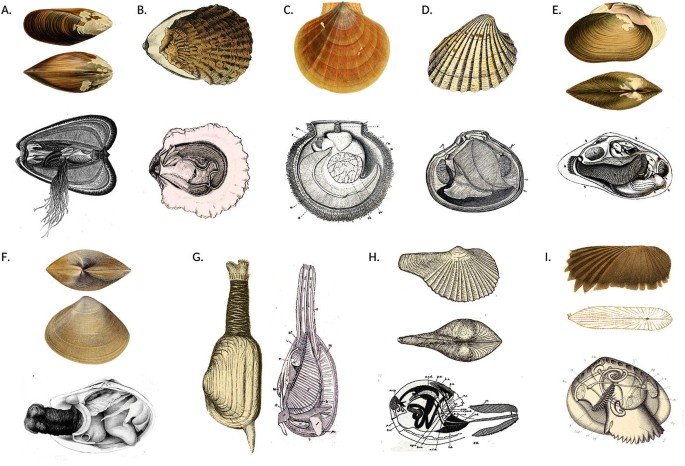
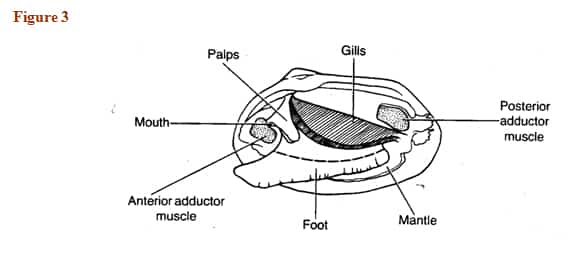
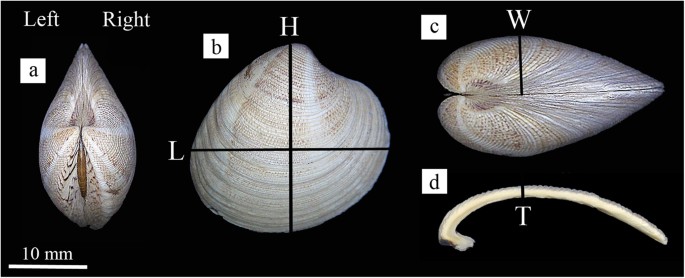
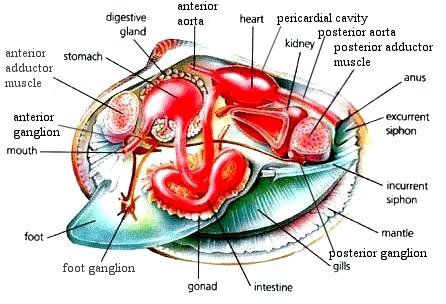
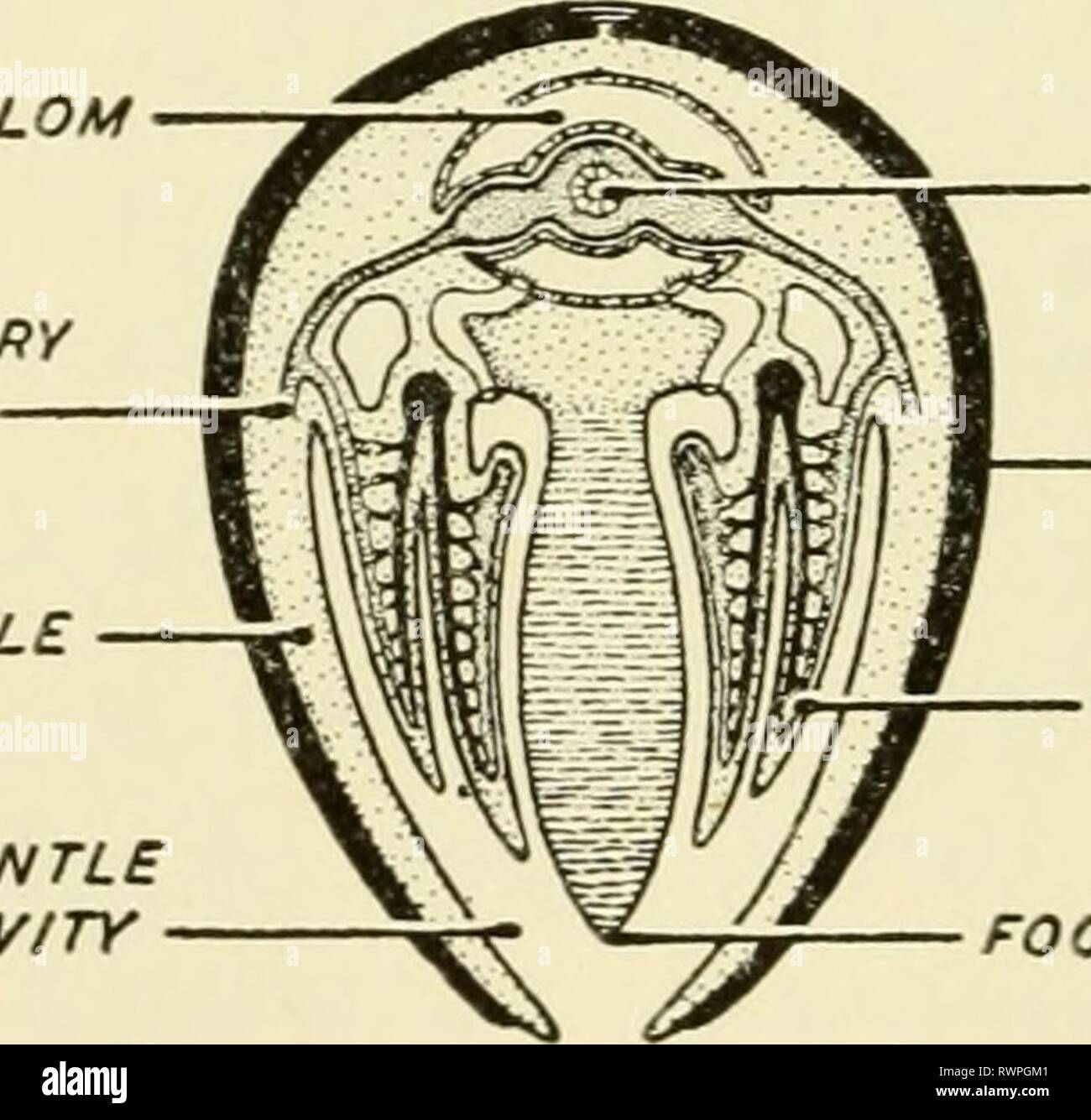
39 internal structures of a clam
biologos.org › articles › flood-geology-and-theFlood Geology and the Grand Canyon: What Does the Evidence ... Jun 29, 2016 · Evidence of periods above sea level is evident from abundant sedimentary structures such as mudcracks, raindrop prints, ripple marks, cross bedding, and small animal tracks (we show many photos of these structures in our chapter Sedimentary Structures, Clues from the Scene of the Crime). 2. DOC Clam Dissection - wallingford.k12.ct.us Continue following the intestine toward the posterior end of the clam. Find the . anus. just behind the posterior adductor muscle. Use your probe to trace the path of food & wastes from the incurrent siphon through the clam to the excurrent siphon. Answer the questions on your lab report & label the diagrams of the internal structures of the clam.
Snapping Hip Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment - Healthline Feb 26, 2018 · Internal. This type occurs when your tendons slide over bone structures at the front of your hip joint. External. ... keeping your feet together. Your legs should resemble a clam shell when opened.

Internal structures of a clam
Bivalve shell - Wikipedia The oldest point of a bivalve shell is called the beak, and the raised area around it is known as the umbo (plural umbones). The hinge area is the dorsum or back of the shell. The lower, curved margin is the ventral side.. The anterior or front of the shell is where the byssus and foot are located (if the animal has these structures) and the posterior or back of the shell is where the … Armstrong's handbook of human resource management practice Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Skeletal Muscle: Definition, Function, Structure, Location | Biology ... Mar 26, 2019 · Skeletal muscle is adapted and shaped in many different ways, which give rise to complex movements. Skeletons are not always internal as they are in humans. Even animals with exoskeletons, like crabs and mussels, have skeletal muscle. While the muscle might be adapted differently depending on the animal, skeletal muscle is defined by its ...
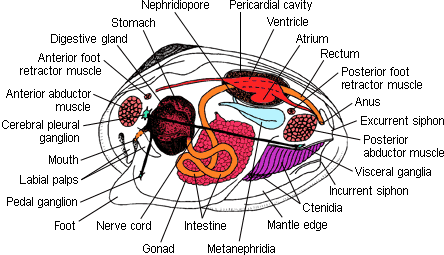
Internal structures of a clam. Clam Anatomy - Clams Ahoy The common hardshell clam Mercenaria mercenaria, better known as a cherrystone, has a mouth, labial palps (antecedents of lips), a stomach, separate digestive gland, an intestine, nerve cord and an anus. The foot of a clam is a curved flesh protrusion from the perimeter of the anterior flesh. Mollusk Facts: Habitat, Behavior, Diet - ThoughtCo Dec 13, 2019 · Description . Any group that embraces squids, clams, and slugs present a challenge when it comes to formulating a general description. There are only three characteristics shared by all living mollusks: the presence of a mantle (the rear covering of the body) that secretes calcareous (e.g., calcium-containing) structures; the genitals and anus opening into … PDF Anatomy of a Clam - University of Florida 11.04 Identify and describe the basic structure and internal anatomy of an oyster or a mussel (SC.3.L.15.1). 12.01 Recognize and observe safety practices necessary in carrying out aquaculture ... Copy the External and Internal Clam Anatomy handouts for each student. 6. Give students a copy of the Introduction to the Biology of Mollusks ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › PolychaetePolychaete - Wikipedia Polychaeta (/ ˌ p ɒ l ɪ ˈ k iː t ə /) is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (/ ˈ p ɒ l ɪ ˌ k iː t s /).Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin.
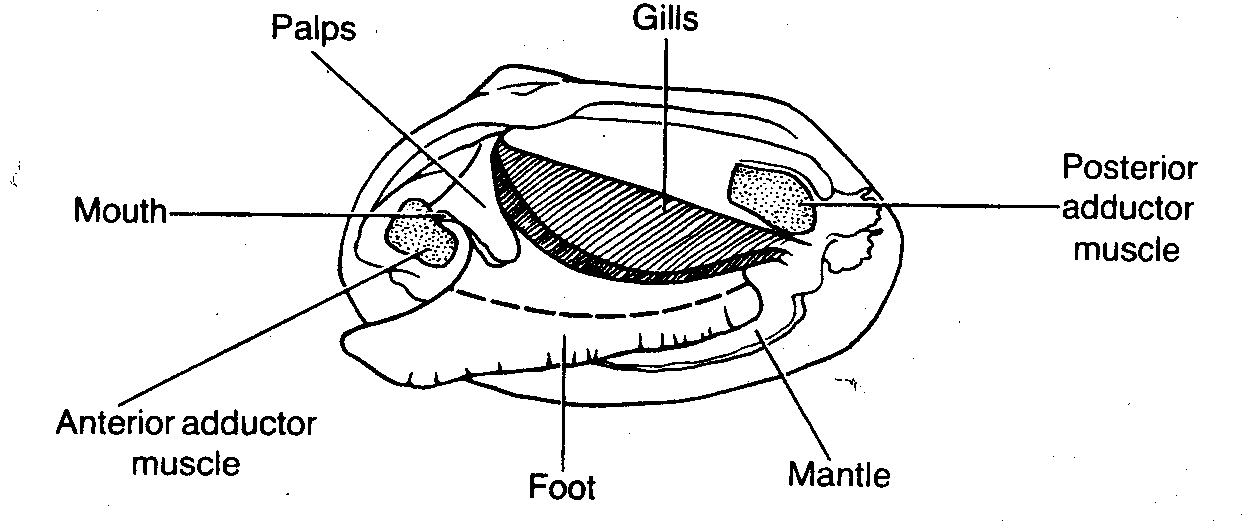
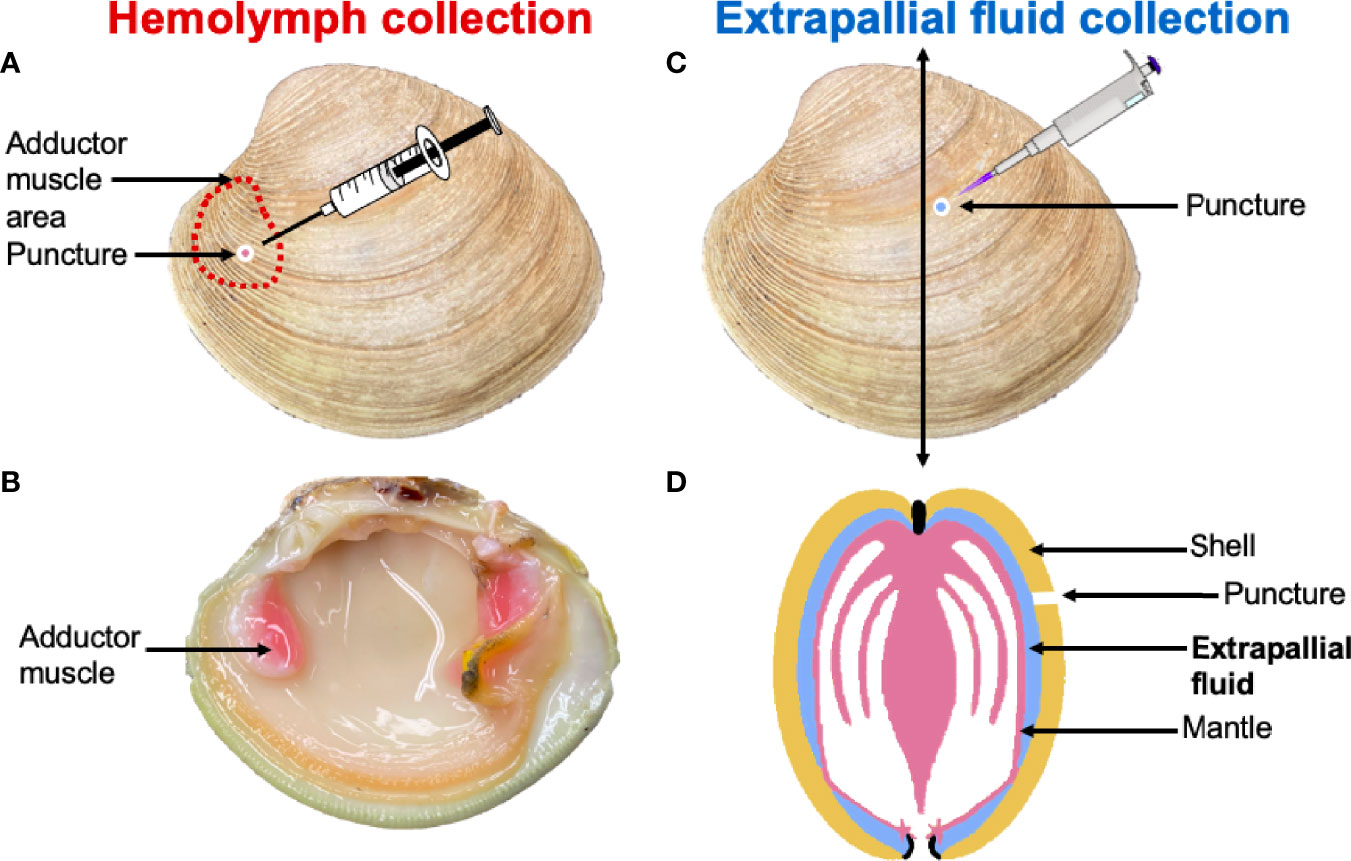
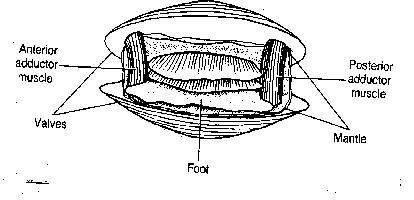
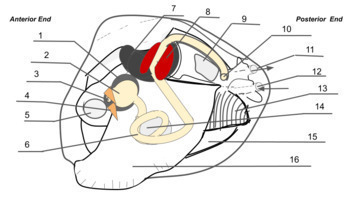
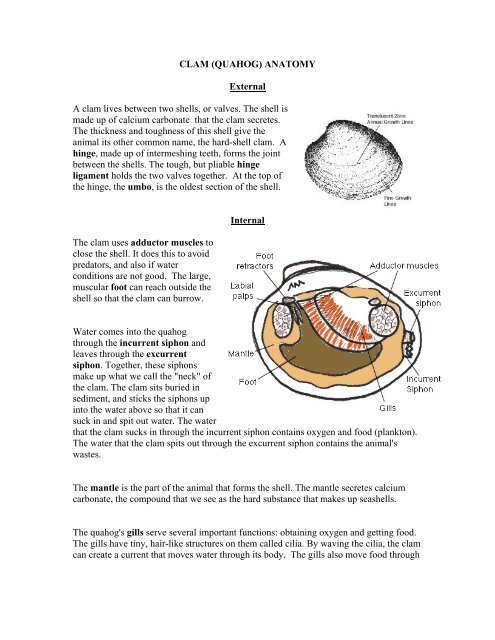
Clam Dissection Clams are marine mollusks with two valves or shells. Like all mollusks, a clam has a mantle which surrounds its soft body. It also has a muscular foot which enables the clam to burrow itself in mud or sand. The soft tissue above the foot is called the visceral mass and contains the clam's body organs. Taxonomy Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Mollusca Clam anatomy and what their organs do by Ethan Enfinger - Prezi One of the most important things in the clam is the gills which allow it to survive underwater. And lastly is the digestive system which as you can guess involves digesting all of the food that the clam eats as well as the liver and the stomach which helps in digesting the food. Conclusion The insides Clam anatomy and what their organs do. Solved 3. Describe what it means for an organism to be | Chegg.com What structures of the internal anatomy of a clam might lead you to conclude that a clam is triploblastic? Expert Answer 100% (5 ratings) Ans) An organism can be called triploblastic when it has three germ layers namely ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Generally, multicellular organisms are only triploblastic and they are bilatera … PDF Taxonomy, Anatomy, and Biology of the Hard Clam Internal Clam 1 Mantle Shell Anatomy • Covers visceral or body mass • Holds in fluid • Secrets new shell 2. Ant. adductor muscle 3. Post adductor musclePost. adductor muscle • Hold valves shut 4. Pericardium cavity • Region covered with thin Region covered with thin, dark membrane • Contains 2-chambered heart and kidney in a fluid-filled sac 5.
Clam Diagram & Parts | What Is a Clam? | Study.com A majority of clams possess bilateral symmetry, in which both shells are of the same size and shape. The shells are made of calcium carbonate. As the clam grows, new calcium carbonate is deposited,... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Horse_hoofHorse hoof - Wikipedia A horse hoof is the lower extremity of each leg of a horse, the part that makes contact with the ground and carries the weight of the animal. It is both hard and flexible. It is a complex structure surrounding the distal phalanx of the 3rd digit (digit III of the basic pentadactyl limb of vertebrates, evolved into a single weight-bearing digit in horses) of each of the four limbs, which is ... EMERGENCY “CLAM SHELL” THORACOTOMY - Emergency … Cardiac arrest after penetrating chest trauma may be an indication for emergency thoracotomy. A successful outcome is possible if the patient has a cardiac tamponade and the definitive intervention is performed within 10 minutes of loss of cardiac output. 1– 3 Wherever possible a patient needing surgery for penetrating chest trauma should be moved to an operating theatre … clam | mollusk | Britannica True clams, in the strict sense, are bivalves with equal shells closed by two adductor muscles situated at opposite ends of the shell, and with a powerful, muscular, burrowing foot. Clams characteristically lie buried from just beneath the surface to depths of about 0.6 metre (2 feet). They rarely travel over the bottom as do some other bivalves.
Clam: internal anatomy (dissection) - YouTube Showing the internal anatomy of a clam
Clams Anatomy - Barnegat Bay Shellfish Clam shells are made up in three layers: Nacreous Layer Prismatic Layer Periostracum Layer Nacreous Layer (nacre) The innermost layer of the shell which touches the clam and connects it to the shell. Also known as "Mother of Pearl", this layer is smooth and made up of soothing material Prismatic Layer
Internal Structure of the Clam 09 3 - YouTube Here is the internal structure of the Clam part 3 for Tim Revell's Bio 2 class Spring 2009.
This Little-Known Peruvian Civilization Built Pyramids as Old as ... Aug 06, 2021 · Colossal pyramid structures in the Americas as ... along with the remains of clam shells and fish bones at the site—as well as a large fishing net that was as old as Caral, found along the coast ...
The hatchery culture of bivalves: a practical manual It consists of two irregular shaped auricles and a ventricle. Anterior and posterior aorta lead from the ventricle and carry blood to all parts of the body. The venous system is a vague series of thin-walled sinuses through which blood returns to the heart. Nervous system The nervous system is difficult to observe without special preparation.
Internal Structure of the Clam 09 2 - YouTube Here is the second part to the Clam dissection for Tim Revell's Bio 2 class Spring 2009.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Bivalve_shellBivalve shell - Wikipedia The anterior or front of the shell is where the byssus and foot are located (if the animal has these structures) and the posterior or back of the shell is where the siphon is located (again, if present— the scallops, for example, do not have siphons). Without being able to view these organs, however, determining anterior and posterior can be ...
PDF Anatomy of a Clam This has a single, "limpet-like" shell on top, which is made of proteins and chitin reinforced with calcium carbonate, and is secreted by a mantle that covers the whole upper surface. The underside of the animal consists of a single muscular "foot".
Preserved Specimens for Dissection Projects Get the preserved specimens or complete dissection kit you need for biology labs. Learn about animal anatomy: frog, cow eye, worm, fetal pig, and more.
PDF Clam Dissection Information Sheet - Internal Anatomy A. Feeding Mechanism of clam. Food in mucous string Water enters the mantle cavity from the rear and is pulled forward by the beating of cilia to the gills and mouth. Water flowing over the gill is filtered, tiny food partic es External are caught in the mucus coating and carried by cilia, gill in a mucus string, to the mouth. Sand and other ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ChitonChiton - Wikipedia Internal anatomy. The girdle is often ornamented with spicules, bristles, hairy tufts, spikes, or snake-like scales. The majority of the body is a snail-like foot, but no head or other soft parts beyond the girdle are visible from the dorsal side. The mantle cavity consists of a narrow channel on each side, lying between the body and the girdle.
Clam study: the shell, the internal anatomy and how they feed Clam study: the shell, the internal anatomy and how they feed Summary Compare different sizes of shells and learn about how shells grow. Dissect a clam and discover that inside a familiar clam shell, often seen on the beach, there is a living animal. Identify the major body parts of a clam, and compare their function to equivalent organs in people.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Noise_pollutionNoise pollution - Wikipedia The ability to detect vibration through mechanosensory structures is most important in invertebrates and fish. Mammals, also, depend on pressure detector ears to perceive the noise around them. Therefore, it is suggested that marine invertebrates are likely perceiving the effects of noise differently than marine mammals.
Clam Dissection - BIOLOGY JUNCTION Clams are marine mollusks with two valves or shells. Like all mollusks, a clam has a mantle which surrounds its soft body. It also has a muscular foot which enables the clam to burrow itself in mud or sand. The soft tissue above the foot is called the visceral mass and contains the clam's body organs. Taxonomy Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Mollusca
Jekyll Island Tours | Trolley Tours, Ghost Tours, Carriage Tours, Eco ... 4-H Tidelands Nature Center 100 S Riverview Dr Jekyll Island, GA 31527 912.635.5032 Canoe & Kayak Tour Agency. Located on the southwest side of Jekyll Island, adjacent to the salt marsh on the pristine 'Tidelands' salt pond, 4-H Tidelands Nature Center offers hands-on coastal ecology programs for the general public and school groups, guided kayak tours, canoe rentals, and a …
Internal Structure of the Clam 09 1 - YouTube Here is the first part of the Clam dissection for Tim Revell's Bio 2 class 2009.
Clam Dissection - JKL Bahweting Middle School Clam Dissection Pre-lab Use your textbook and the websites provided in Resources to answer the following questions in your lab notebook. 1. Give the kingdom, phylum, and class for the clam. ... Label the internal structures of the clam and draw red arrows showing the pathway of food as it travels to the clam's stomach: Click on image to enlarge.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › MolluscaMollusca - Wikipedia Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (/ ˈ m ɒ l ə s k /).Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized.
Northwest Indian Fisheries Commission (NWIFC) | Serving the … Sep 06, 2022 · After many years of planning, the Swinomish Indian Tribal Community has laid the foundation for the first known modern clam garden in the country. Over two days in August, community members and invited guests passed rocks from hand to hand to build a 2-foot-high, 200-foot-long rock wall on the shore of Kukutali Preserve. “The rock […]
Skeletal Muscle: Definition, Function, Structure, Location | Biology ... Mar 26, 2019 · Skeletal muscle is adapted and shaped in many different ways, which give rise to complex movements. Skeletons are not always internal as they are in humans. Even animals with exoskeletons, like crabs and mussels, have skeletal muscle. While the muscle might be adapted differently depending on the animal, skeletal muscle is defined by its ...
Armstrong's handbook of human resource management practice Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Bivalve shell - Wikipedia The oldest point of a bivalve shell is called the beak, and the raised area around it is known as the umbo (plural umbones). The hinge area is the dorsum or back of the shell. The lower, curved margin is the ventral side.. The anterior or front of the shell is where the byssus and foot are located (if the animal has these structures) and the posterior or back of the shell is where the …

















Post a Comment for "39 internal structures of a clam"