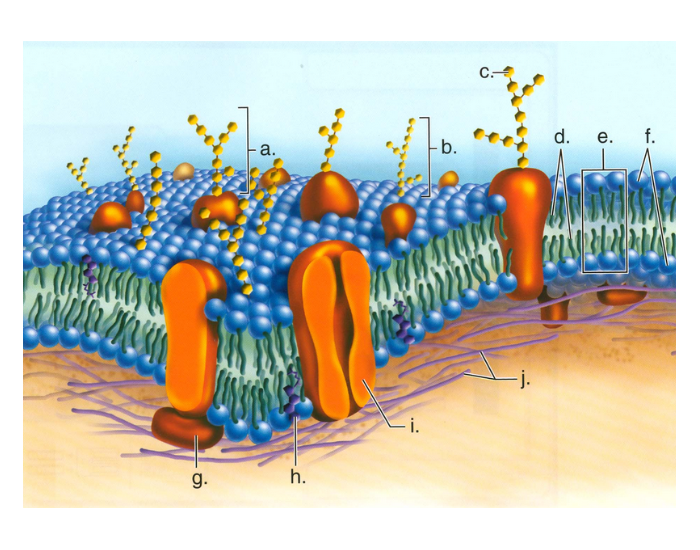
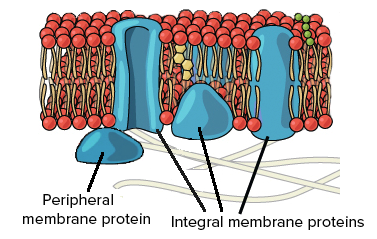
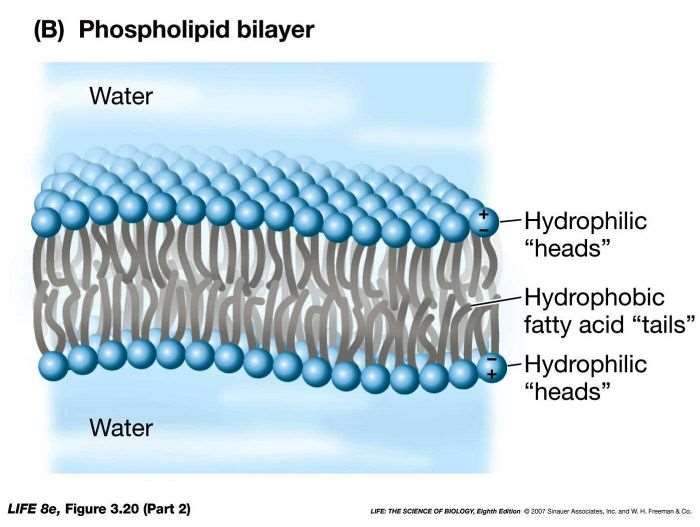
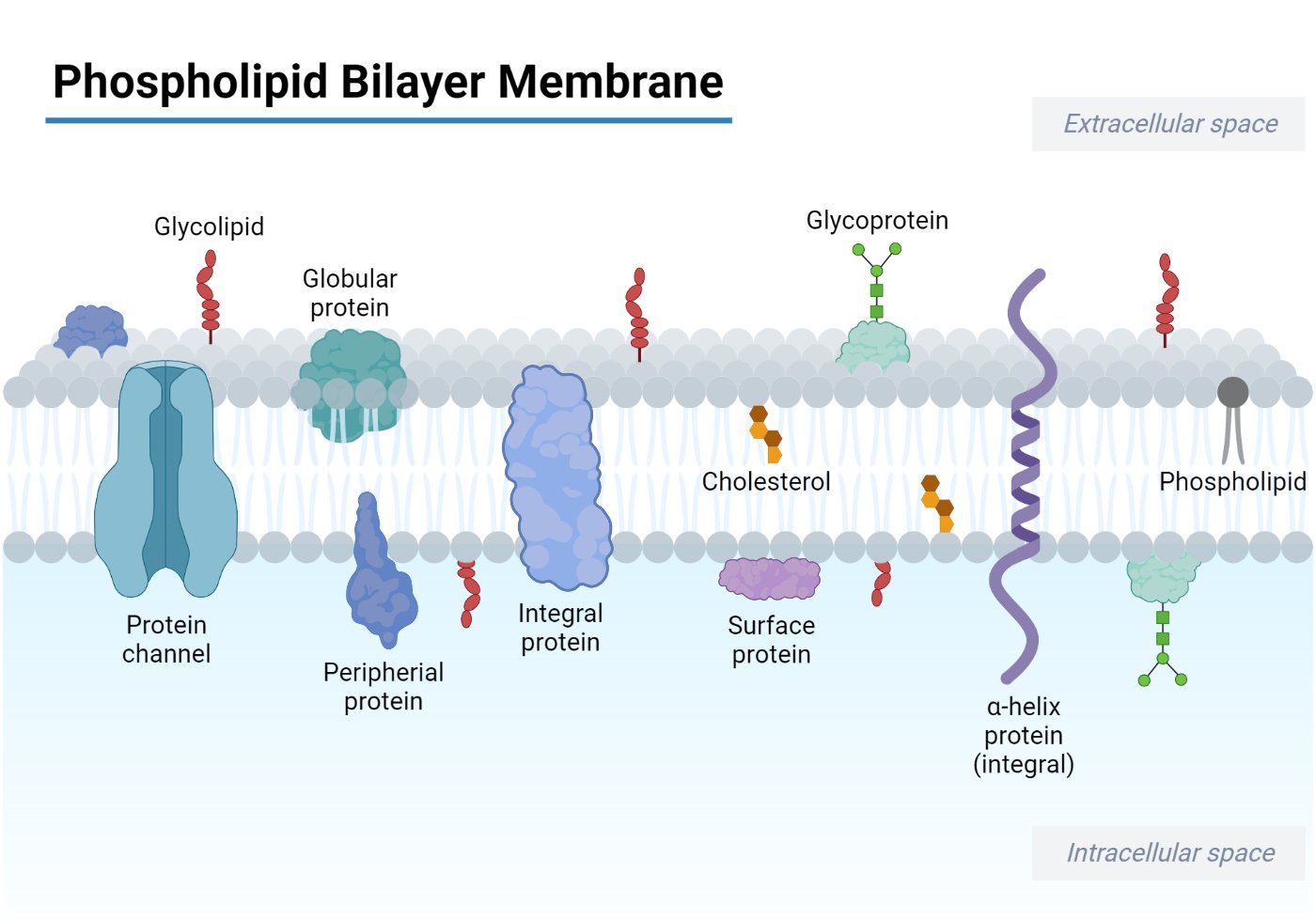
39 phospholipid bilayer diagram labeled
Omega-3s and Phospholipids: How Are They Linked? - Healthline Aug 25, 2020 · Phospholipids are a type of fat present in plant and animal cells. They can also be found in certain omega-3 dietary supplements. This article discusses the functions of phospholipids,... › health › nutritionOmega-3s and Phospholipids: How Are They Linked? - Healthline Aug 25, 2020 · Phospholipids are a type of fat present in plant and animal cells. They can also be found in certain omega-3 dietary supplements. This article discusses the functions of phospholipids,...
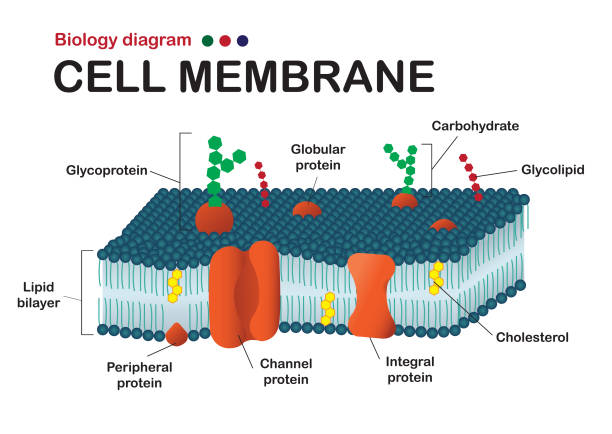
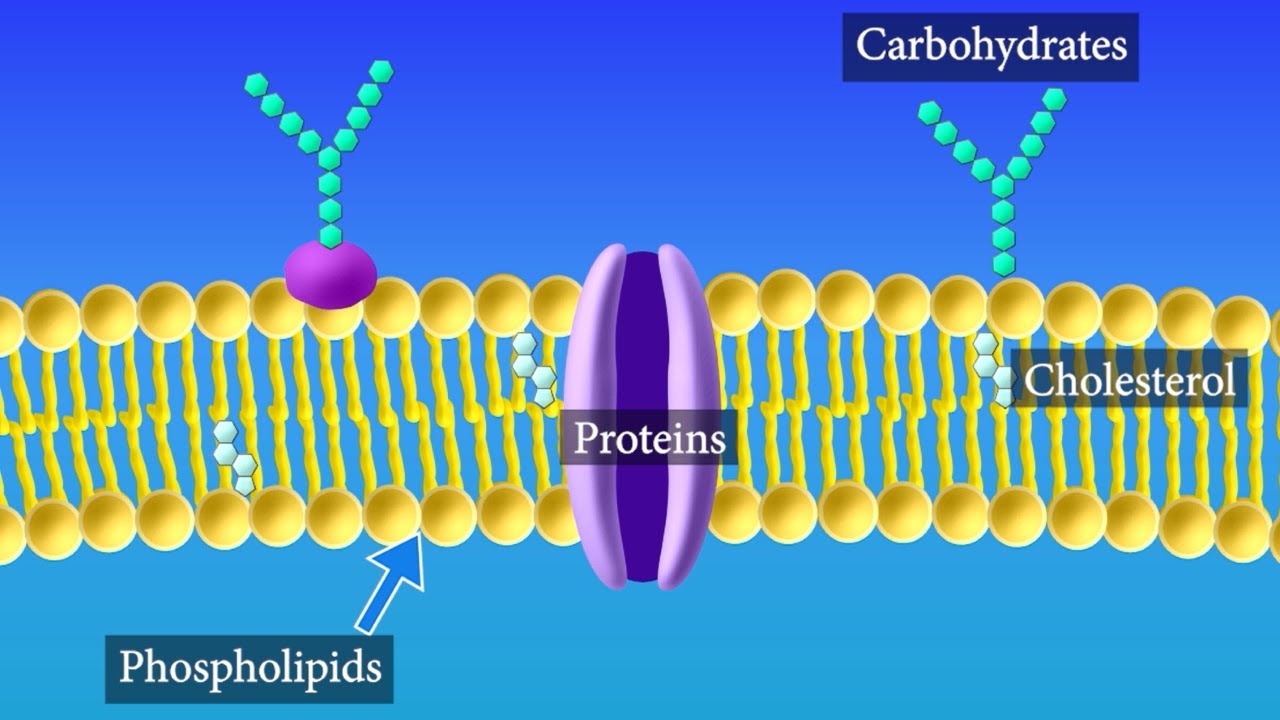
Phospholipid - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Phospholipids are amphiphilic molecules with hydrophobic fatty acid chains and hydrophilic moieties. They occur naturally in all living organisms as the major components of cell membranes. Various phospholipid classes with different polar moieties are found in nature. pH greatly affects the association of the polar moieties in phospholipids.
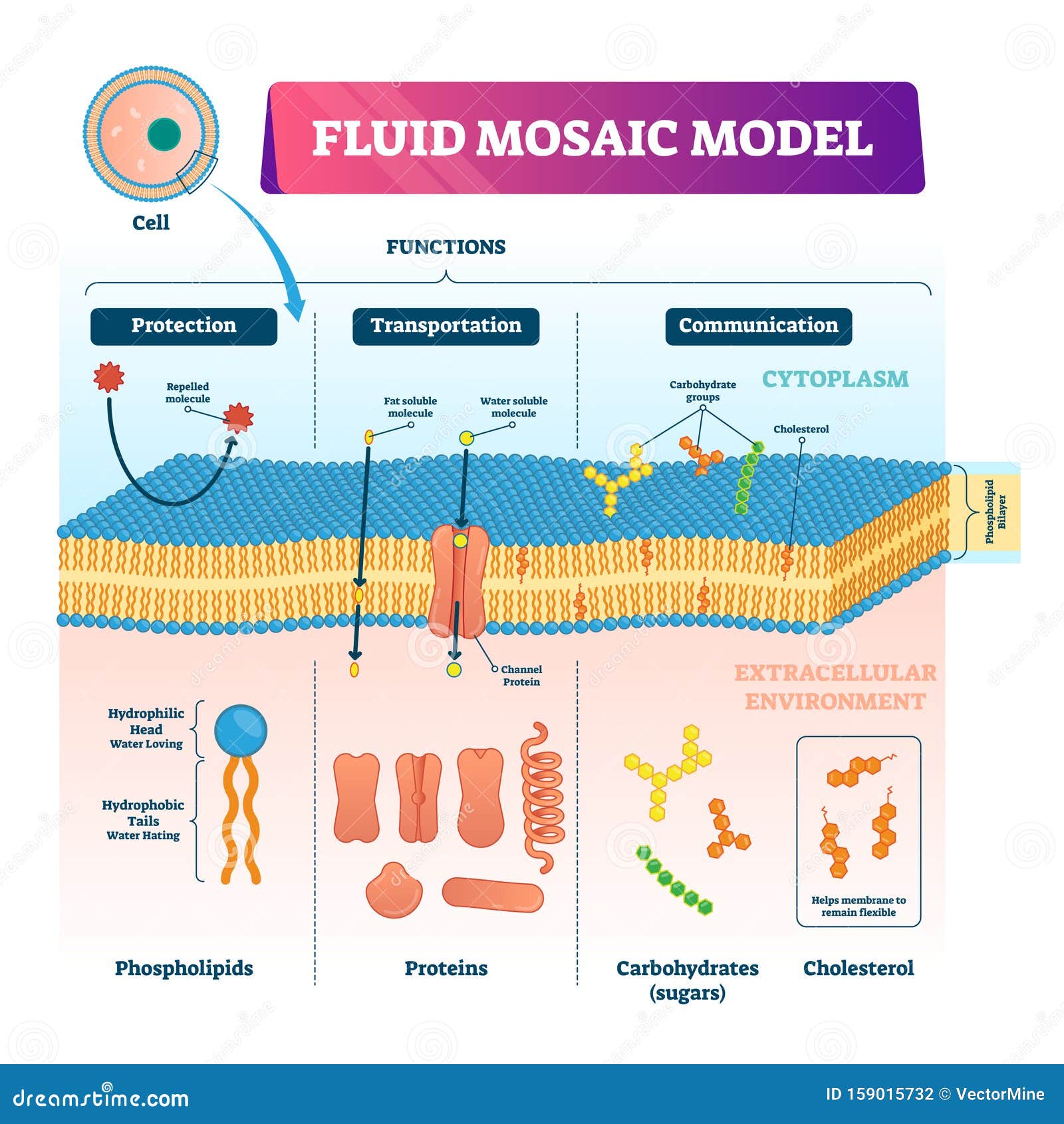
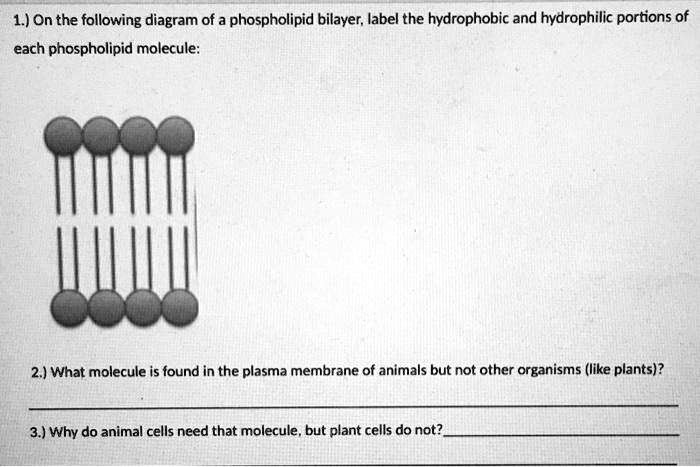
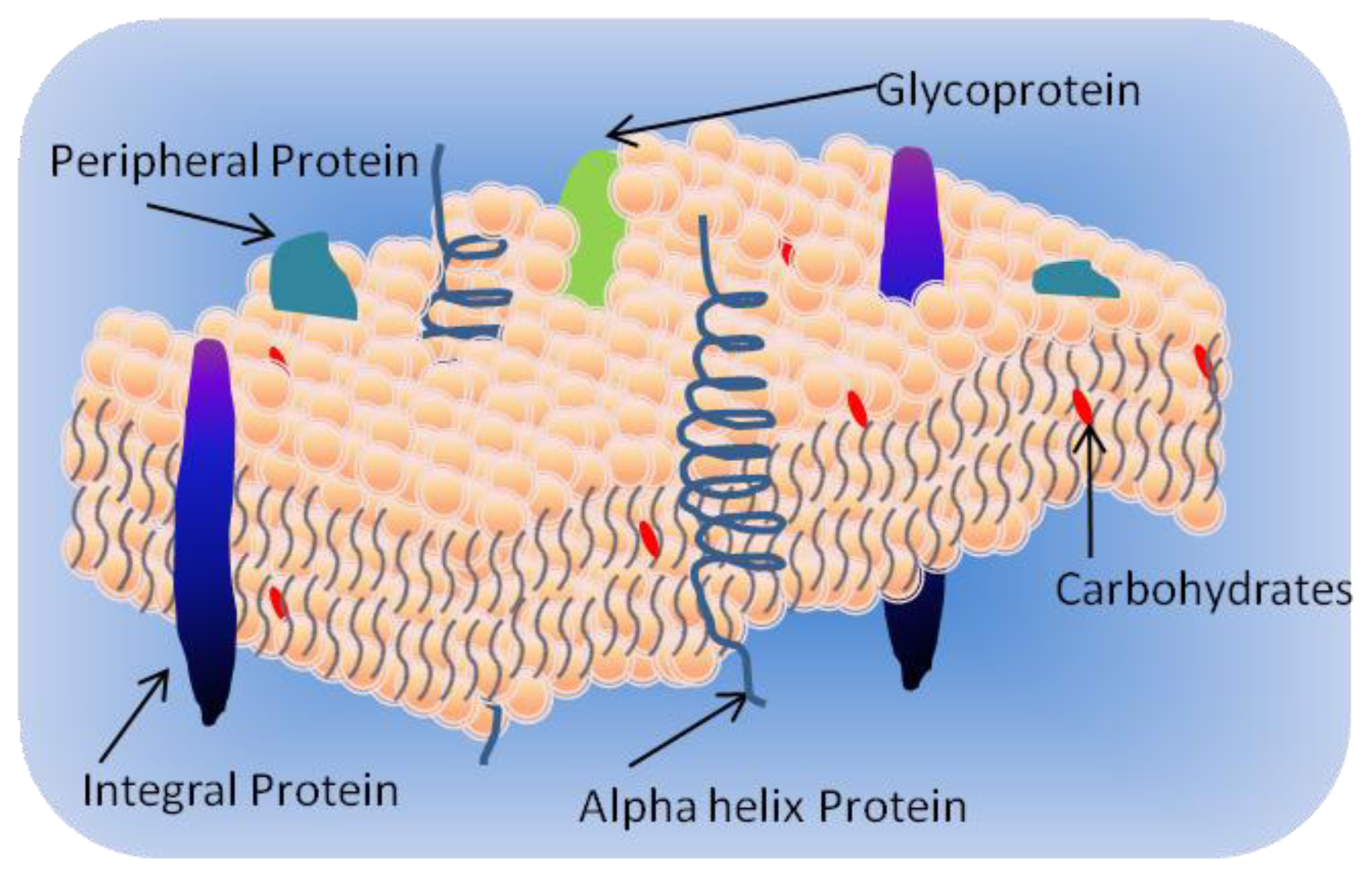
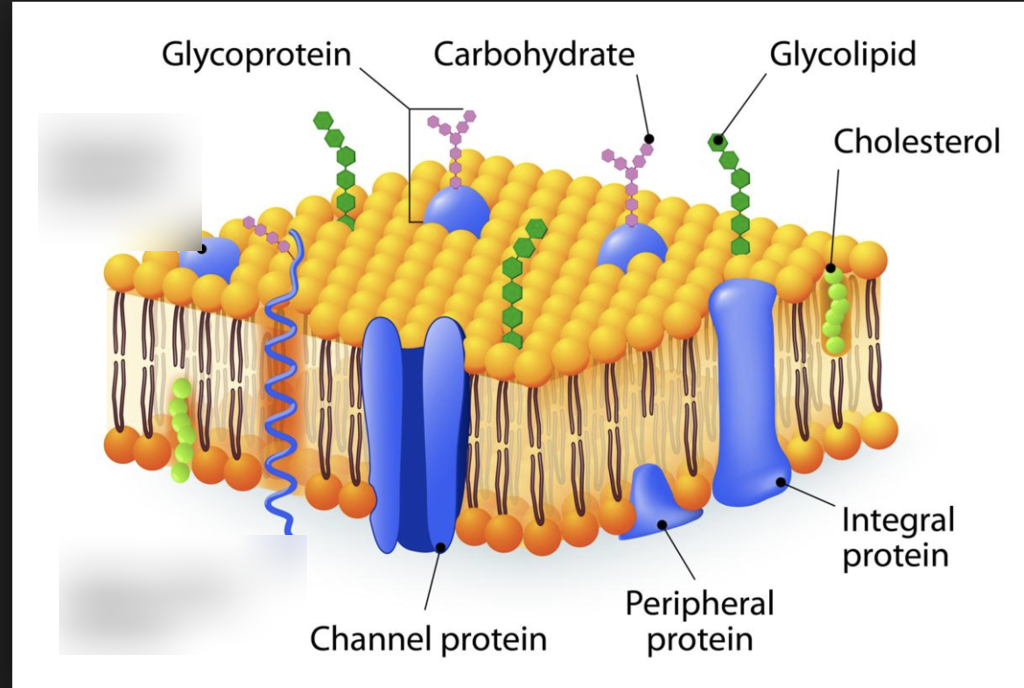
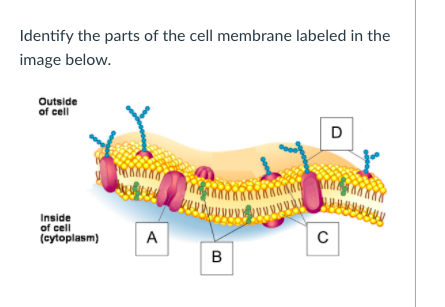
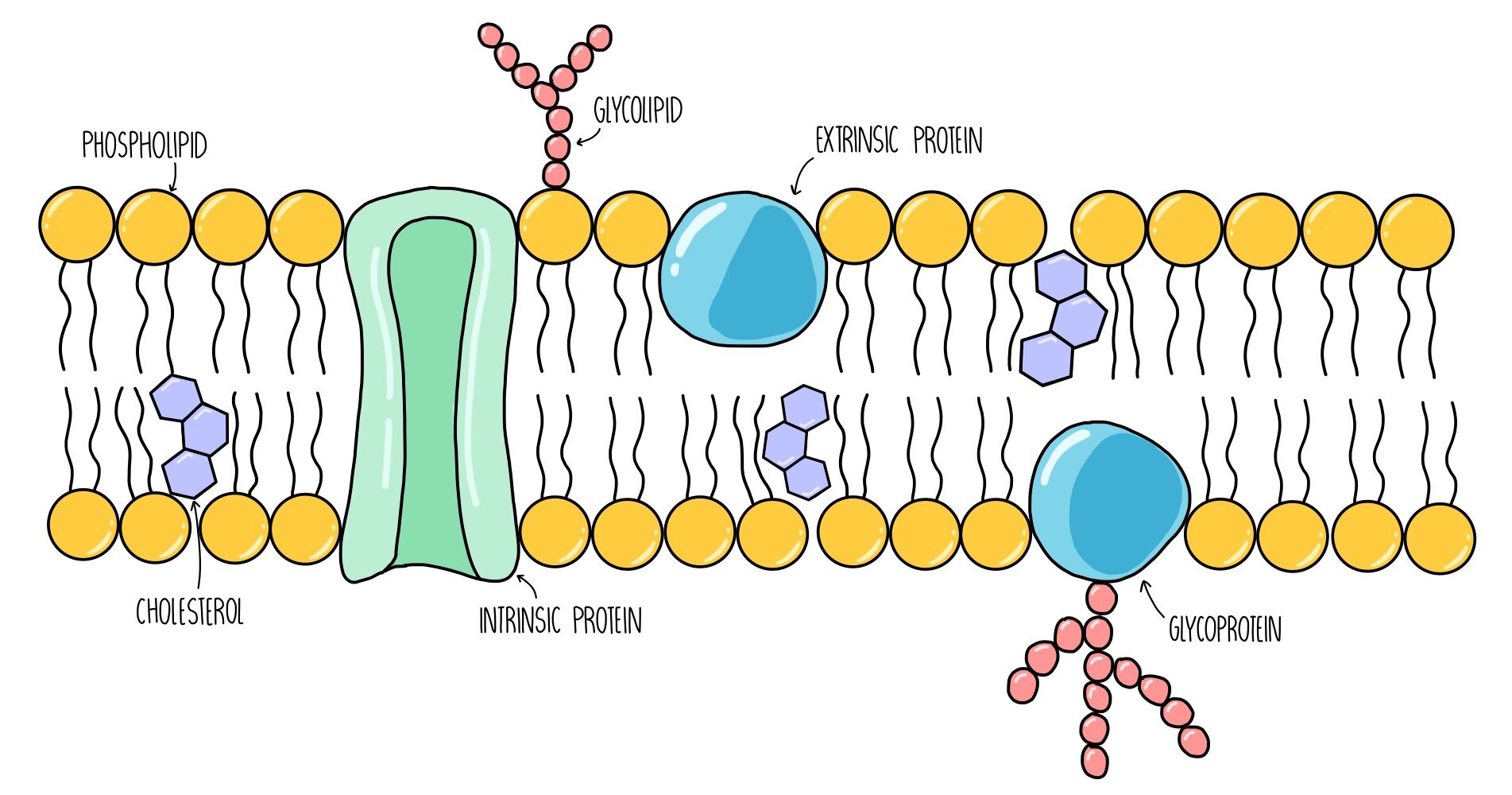
Phospholipid bilayer diagram labeled
Antiphospholipid syndrome - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Feb 25, 2022 · Antiphospholipid (AN-te-fos-fo-LIP-id) syndrome is a condition in which the immune system mistakenly creates antibodies that attack tissues in the body. These antibodies can cause blood clots to form in arteries and veins. Blood clots can form in the legs, lungs and other organs, such as the kidneys and spleen. › dictionary › phospholipidPhospholipid Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster phospholipid. noun. phos· pho· lip· id -ˈlip-əd. variants also phospholipide. -ˌīd. : any of various phosphorus-containing complex lipids (such as lecithins and phosphatidylethanolamines) that are derived from glycerol and are major constituents of the membranes of cells and intracellular organelles and vesicles. › topics › agricultural-and-biological-sciencesPhospholipid - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Phospholipids are amphiphilic molecules with hydrophobic fatty acid chains and hydrophilic moieties. They occur naturally in all living organisms as the major components of cell membranes. Various phospholipid classes with different polar moieties are found in nature. pH greatly affects the association of the polar moieties in phospholipids.
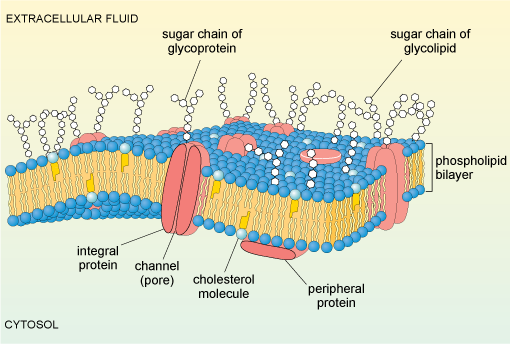
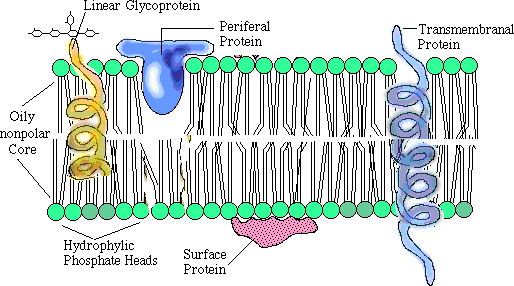
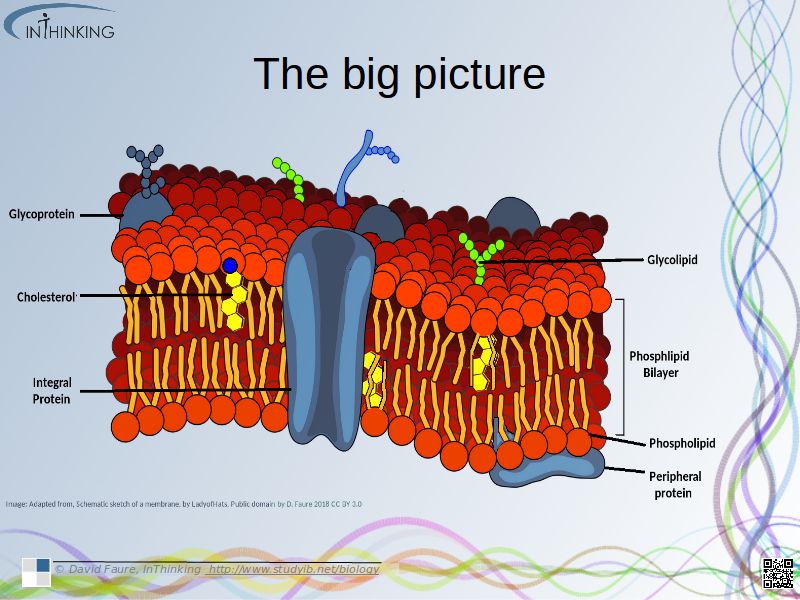
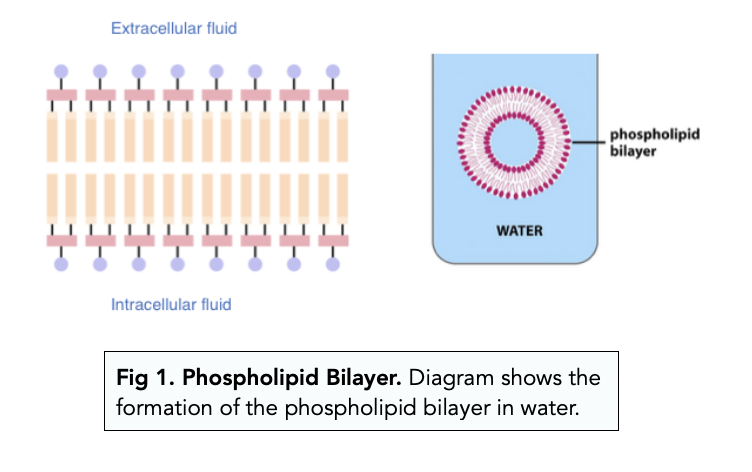
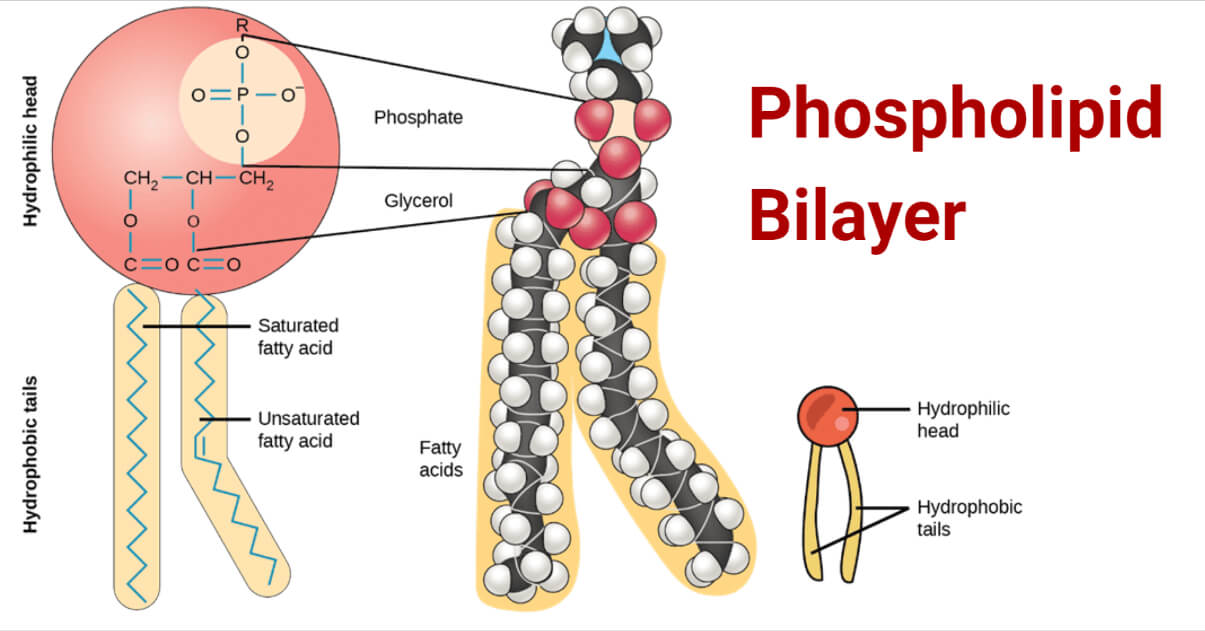
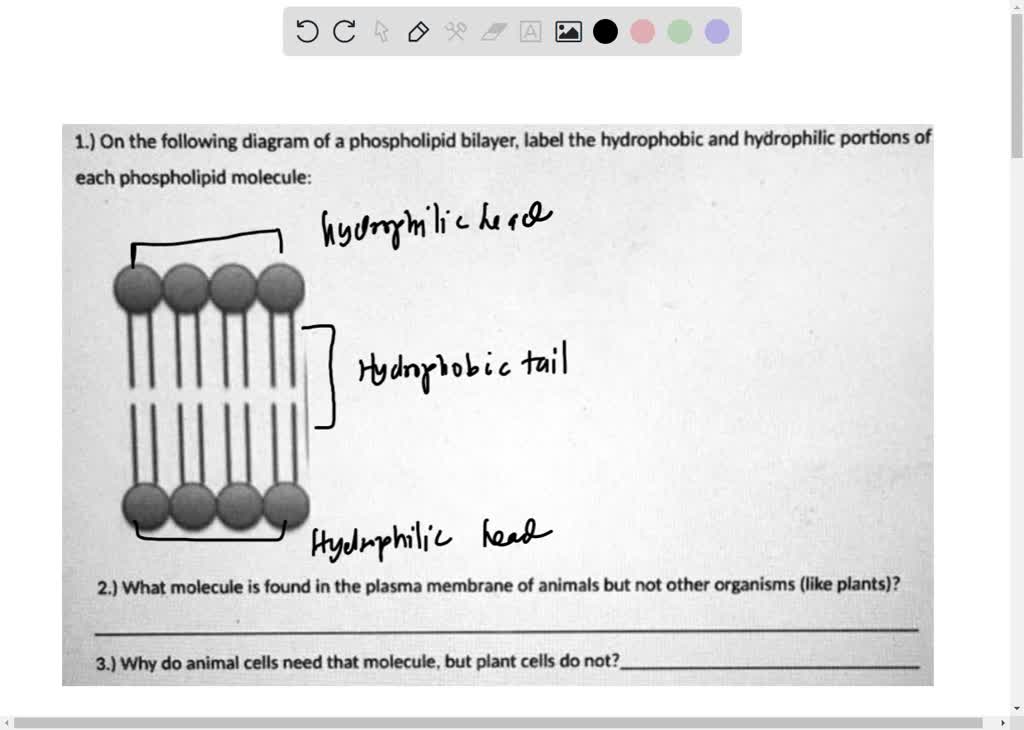
Phospholipid bilayer diagram labeled. Phospholipids - Types, Functions and their Properties - An … Phospholipids are compound lipids, consisting of phosphoric acids, nitrogen base, alcohol and fatty acids. These compound lipids are major components of the cell membrane and also provide a fluid character to the membranes. In cell membranes, these phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, which forms the inside of the bilayer. Phospholipid - Wikipedia Phospholipids [1] are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. [2] Phospholipid Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster phospholipid. noun. phos· pho· lip· id -ˈlip-əd. variants also phospholipide. -ˌīd. : any of various phosphorus-containing complex lipids (such as lecithins and phosphatidylethanolamines) that are derived from glycerol and are major constituents of the membranes of cells and intracellular organelles and vesicles. › diseases-conditions › antiphospholipid-syndromeAntiphospholipid syndrome - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic Feb 25, 2022 · To confirm a diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome, the antibodies must appear in your blood at least twice, in tests conducted 12 or more weeks apart. You can have antiphospholipid antibodies and never develop signs or symptoms. A diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome is made only when these antibodies cause health problems. Treatment
scienceterms.net › biology › phospholipidPhospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function, Examples - Science... Mar 13, 2019 · Phospholipid Definition. A phospholipid is an amphiphilic molecule consisting of a polar head region, a unit of glycerol, and two or more non-polar fatty acid tails, typically found in a cell membrane. A bilayer of phospholipid molecules forms a plasma membrane. › diseases-conditions › antiphospholipid-syndromeAntiphospholipid syndrome - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Feb 25, 2022 · Antiphospholipid (AN-te-fos-fo-LIP-id) syndrome is a condition in which the immune system mistakenly creates antibodies that attack tissues in the body. These antibodies can cause blood clots to form in arteries and veins. Blood clots can form in the legs, lungs and other organs, such as the kidneys and spleen. Antiphospholipid syndrome - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic Feb 25, 2022 · To confirm a diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome, the antibodies must appear in your blood at least twice, in tests conducted 12 or more weeks apart. You can have antiphospholipid antibodies and never develop signs or symptoms. A diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome is made only when these antibodies cause health problems. … Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function, Examples - Science … Mar 13, 2019 · Phospholipid Definition. A phospholipid is an amphiphilic molecule consisting of a polar head region, a unit of glycerol, and two or more non-polar fatty acid tails, typically found in a cell membrane. A bilayer of phospholipid molecules forms a plasma membrane.
Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function | Biology Dictionary Oct 4, 2019 · A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. Lipids are molecules that include fats, waxes, and some vitamins, among others. Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule. Phospholipid | biochemistry | Britannica phospholipid, also called Phosphatide, any member of a large class of fatlike, phosphorus-containing substances that play important structural and metabolic roles in living cells. The phospholipids, with the sphingolipids, the glycolipids, and the lipoproteins, are called complex lipids, as distinguished from the simple lipids (fats and waxes) and from other fat-soluble cell … byjus.com › biology › phospholipidPhospholipids - Types, Functions and their Properties - An... Phospholipids are compound lipids, consisting of phosphoric acids, nitrogen base, alcohol and fatty acids. These compound lipids are major components of the cell membrane and also provide a fluid character to the membranes. In cell membranes, these phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, which forms the inside of the bilayer. › topics › agricultural-and-biological-sciencesPhospholipid - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Phospholipids are amphiphilic molecules with hydrophobic fatty acid chains and hydrophilic moieties. They occur naturally in all living organisms as the major components of cell membranes. Various phospholipid classes with different polar moieties are found in nature. pH greatly affects the association of the polar moieties in phospholipids.
› dictionary › phospholipidPhospholipid Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster phospholipid. noun. phos· pho· lip· id -ˈlip-əd. variants also phospholipide. -ˌīd. : any of various phosphorus-containing complex lipids (such as lecithins and phosphatidylethanolamines) that are derived from glycerol and are major constituents of the membranes of cells and intracellular organelles and vesicles.
Antiphospholipid syndrome - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Feb 25, 2022 · Antiphospholipid (AN-te-fos-fo-LIP-id) syndrome is a condition in which the immune system mistakenly creates antibodies that attack tissues in the body. These antibodies can cause blood clots to form in arteries and veins. Blood clots can form in the legs, lungs and other organs, such as the kidneys and spleen.















Post a Comment for "39 phospholipid bilayer diagram labeled"